|
| |
Buffer solutions: To control pH values in electrolytes.
!------------------------------------------------------!
$buffer-solutions
optional !
buffer-name
character
required !
number-of-ions
integer
required !
ion-valency
double_array required
!
ion-name-1
character
required !
ion-name-2
character
required !
ion-name-3
character
optional ! (only necessary for some buffers,
e.g. PBS)
ion-name-4
character
optional !
pKa
double_array required
!
dpKa_dT
double_array required
!
z_acid
double_array
required !
$end_buffer-solutions
optional !
!------------------------------------------------------!
Syntax
! name of buffer
buffer-name = ACETATE
! -Na+
+ CH3COOH)
= HEPES
!
= TRIS
!
= MOPS
!
= PBS
!
! number of ions that are contained in the buffer
number-of-ions = 2
! 2 ACETATE,
HEPES,
TRIS and MOPS
= 4
! 4 for PBS
! valency
of the ions that are contained in the buffer
ion-valency = -1d0 +1d0
!
ACETATE: (CH3COO)- Na+
= +1d0 -1d0
! for
TRIS: TrisH+
(OH)-
= -1d0 +1d0
! for
MOPS: (C7H14NO4S)-
Na+
= -1d0 -2d0 -3d0 1d0
! for PBS: (H2PO4)-
(HPO4)2- (PO4)3-
Na+
! (the number of expected entries corresponds to number-of-ions)
! name of the ions that are contained in the buffer
!
! CH3COOH <==> (CH3COO)-
+ H+
ion-name-1 = CH3COO^-
! ACETATE)
ion-name-2 = Na^+
! ACETATE)
!
!
TrisH+ <==> Tris
+ H+
( "NH3+" <==>
"NH2" + H+
)
! Tris + H20 <==> TrisH+
+ (OH)- (
"NH2" + H20 <==> "NH3+"
+ (OH)- )
ion-name-1 = TrisH^+
! TRIS)
ion-name-2 = OH^-
! TRIS)
!
("SO3H" <==>
"(SO3)-" +
H+)
ion-name-1 = Mops^-
! MOPS)
C7H15NO4S <==> (C7H14NO4S)-
+ H+
ion-name-2 = Na^+
! MOPS)
ion-name-1 = H2PO4^-
! PBS)
NaH2PO4 <==> (H2PO4)-
+ Na+
ion-name-2 = HPO4^2-
! PBS)
Na2HPO4 <==> (HPO4)2-
+ 2 Na+
ion-name-3 = PO4^3-
! PBS)
(HPO4)2- <==> (PO4)3-
+ H+
ion-name-4 = Na^+
! PBS)
! pKa value(s) of buffer reactions
!
! the concentrations of acid and base (Henderson-Hasselbalch equation):
! pH =
+ log10 ([base]/[acid])
! Example: pH = pKa + log10
([ Cl- ]/[ HCl ])
! HCl + H20
<==> Cl- + H30+
pKa =
4.76d0
! for ACETATE: pKa
at 25░ C ( = 298.15 K)
=
7.66d0
! HEPES: pKa
at 25░ C ( = 298.15 K)
= 8.06d0
! TRIS: pKa
at 25░ C ( = 298.15 K)
= 7.31d0
! MOPS: pKa
at 25░ C ( = 298.15 K)
= 2.15d0 7.21d0
12.33d0 ! PBS: pKa,1 pKa,2 pKa,3
at 25░ C ( = 298.15 K)
! d pKa / d T value(s) of pKa
value(s), i.e. temperature dependence of pKa value(s)
!
!
!
$electrolyte.
dpKa_dT =
-0.0002d0
! ACETATE: d pKa
/ d T
=
-0.014d0
! HEPES: d pKa
/ d T
= -0.028d0
! TRIS: d pKa / d T
= -0.011d0
! MOPS: d pKa / d T
= 0.0044d0 -0.0028d0 -0.026d0 !
PBS: d pKa,1 / d T d
pKa,2 / d T d
pKa,3 / d T
! charge on the conjugate acid species
! + H20
<==> 'conjugate base' + H30+
! This value enters the equation for the ionic strength dependence
! of the pKa value (modified pKa
value: pKa' ).
z_acid =
0d0
!
ACETATE: 0
= CH3COOH
=
0d0
!
MOPS: 0
= C7H15NO4S
= +1d0
!
TRIS: +1 =
TrisH+
= 0d0 -1d0
-2d0 ! PBS:
0 = H3PO4,
-1 = (H2PO4)-
, -2 = (HPO4)2-
Examples: Acetate, MOPS and PBS (phosphate buffer)
The phosphate buffer is special (and thus more complicated) because it
consists of three pKa values (and it thus has four different
ions).
!------------------------------------------------!
$buffer-solutions
!
!
buffer-name = ACETATE
! Acetate (sodium acetate + acetic acid) (CH3COO-Na+
+ CH3COOH)
number-of-ions = 2
! <==> (CH3COO)-
+ H+
ion-valency = -1d0 +1d0
!
ion-name-1 = CH3COO^-
! -
ion-name-2 = Na^+
!
pKa =
4.76d0
!
dpKa_dT =
-0.0002d0
!
z_acid =
0d0
! 0
= CH3COOH)
!
!
buffer-name = MOPS
!
number-of-ions = 2
!
ion-valency = -1d0 +1d0
! -
Na+
ion-name-1 =
Mops^-
! C7H15NO4S <==> (C7H14NO4S)-
+ H+
ion-name-2 = Na^+
!
pKa =
7.31d0
!
! (Note: This pKa is thermodynamic value. The working pKa'
is 7.20.)
dpKa_dT =
-0.011d0
!
z_acid =
0d0
! 0
= C7H15NO4S)
!
!
buffer-name = PBS
!
number-of-ions = 4
!
ion-valency = -1d0 -2d0
-3d0 1d0 !
-
(HPO4)2- (PO4)3-
Na+
ion-name-1 =
H2PO4^-
! NaH2PO4 <==> (H2PO4)-
+ Na+
ion-name-2 = HPO4^2-
! <==> (HPO4)2-
+ 2 Na+
ion-name-3 = PO4^3-
!
ion-name-4 = Na^+
!
pKa =
2.15d0 7.21d0
12.33d0 !
dpKa_dT =
0.0044d0 -0.0028d0 -0.026d0 !
z_acid =
0d0 -1d0
-2d0 ! 0 = H3PO4,
-1 = (H2PO4)-
, -2 = (HPO4)2-)
!
$end_buffer-solutions
!
!------------------------------------------------!
For more details on buffers, please have a look at the excellent book of
R.J. Beynon, J.S. Easterby, "Buffer solutions: The basics", Oxford University
Press (1996).
Rob Beynon also provides a web interface "A recipe calculator for
thermodynamically correct buffers for pH control" at:
http://www.liv.ac.uk/buffers/
Example: Acetate buffer (sodium acetate + acetic acid)
- The following figure shows the pH value as a function of the
concentration of the (CH3COO)
- ions.
Note that this number is equal to the concentration of Na+ ions
(see equations above).
The concentration of the acetate buffer is 0.1 M, i.e. it consists of
- 0.1 M CH3COOH (acetic acid) and
- 0.1 M CH3COO-Na+
(sodium acetate).
The temperature was set to 298.15 K ( = 25░ C).
The pKa value at 25░ C is 4.76. Note that the pKa
value depends on temperature and ionic strength. Thus for each pH value a
different value of pKa had been calculated
self-consistently => pKa'.
The nextnano│ calculations were performed by looping over the pH
values. Note that the code adds the appropriate concentrations of Cl-
ions (originating from the acid HCl) and Na+ ions (originating
from the base NaOH) automatically.
CH3COO-
+ H3O+ + Cl-
<==> CH3COOH +
H2O + Cl-
CH3COOH + Na+
+ OH- <==> CH3COO-
+ H2O + Na+
The acetate buffer has the best buffering range (i.e. pH = +-1)
at around pKa = 4.76, i.e. it buffers nicely between pH =
3.76 and pH = 5.76.
Below the pH value of 3, the concentration of (CH3COO)-
is negligible and only CH3COOH exists.
Above the pH value of 8, the concentration of CH3COOH is
negligible and only (CH3COO)- exists.
pH value vs. [CH3COO-]
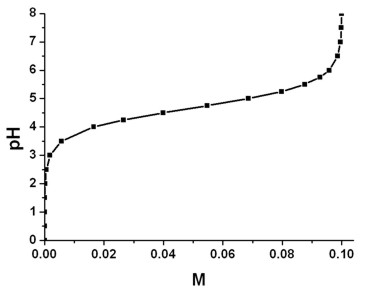
The relation between the pH value, the pKa' value and the
concentration of CH3COO- ions is governed
by the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
pH = pKa' + log (
[CH3COO-] / [CH3COOH] )
The concentration of all ions (not only the buffer ions), the ionic
strength, as well as the pKa' value(s) as a function of pH
are contained in this file:
BufferIonConc_vs_pH1D.dat
If you want to obtain the nextnano│ input file (Buffer_Acetate.in)
that calculates the above figure, please submit a support ticket.
Details on the calculations:
ACETATE (sodium acetate +
acetic acid)
[CH3COOH] =
[ACETATE] / ( 1 + 10pH-pKa )
[(CH3COO)-] = [CH3COOH]
* 10pH-pKa !
Henderson-Hasselbalch equation
[Na+]
= [(CH3COO)-]
MOPS
[C7H15NO4S] =
[MOPS] / ( 1 + 10pH-pKa )
[(C7H14NO4S)-] = [C7H15NO4S]
* 10pH-pKa !
Henderson-Hasselbalch equation
[Na+]
= [(C7H14NO4S)-]
(analogous for HEPES and
TRIS)
PBS (phosphate buffer)
[H3PO4] = [PBS] / ( 1 + 10pH-pKa,1
* ( 1 + 10pH-pKa,2 * ( 1 + 10pH-pKa,3
) ) )
[(H2PO4)-] = [H3PO4]
* 10pH-pKa,1
! Henderson-Hasselbalch equation
[(HPO4)2-] = [(H2PO4)-]
* 10pH-pKa,2
! Henderson-Hasselbalch equation
[(PO4)3-] = [(HPO4)2-]
* 10pH-pKa,3
! Henderson-Hasselbalch equation
[Na+] = (1 * [(H2PO4)-]
+ 2 * [(HPO4)2-] + 3 * [(PO4)3-]
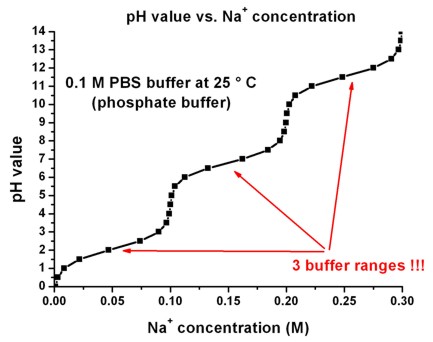
The following figure shows the pH value as a functions of the Na+
concentration for a PBS buffer. Note that there are
three buffer ranges.
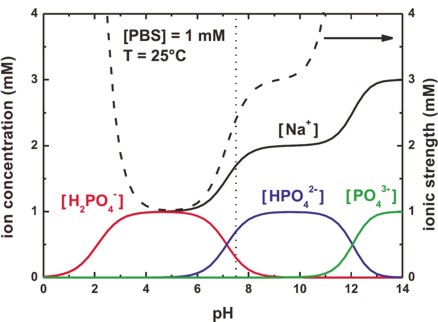
In this figure, we plot the concentration of the PBS buffer ions, and the
resulting ionic strength as a function of pH.
If you want to obtain the nextnano│ input file (Buffer_PBS.in)
that calculates the above figure, please submit a support ticket.
The entries for $buffer-solutions
that are specified in the database can be overwritten in the input
file. For details, have a look at the input file keyword
$buffer-solutions.
|